Understanding Subdural Hematoma: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
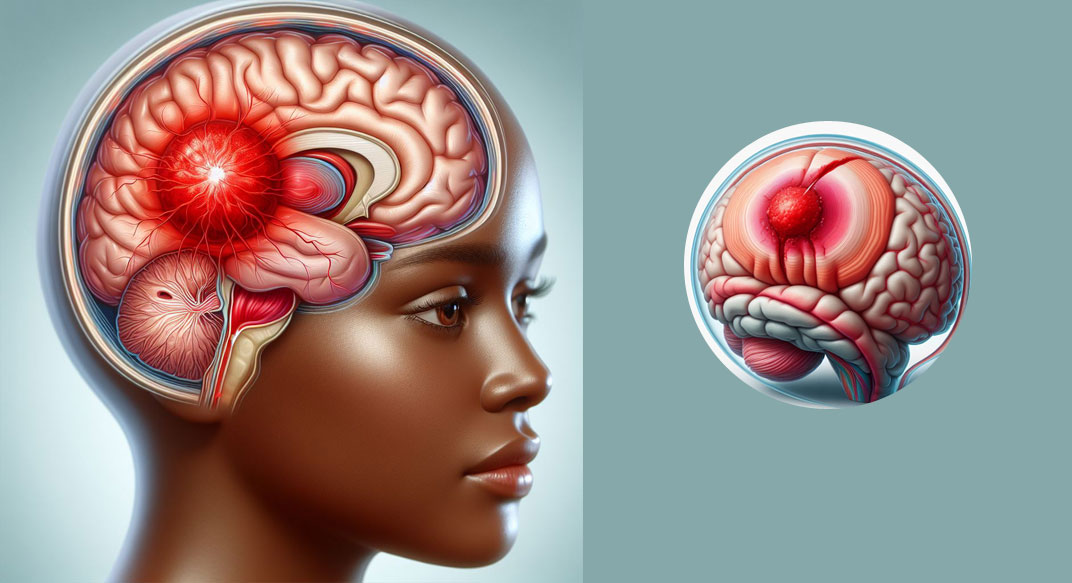
A subdural hematoma is a serious condition characterized by the accumulation of blood between the brain's surface and its outermost covering, the dura mater. This bleeding can put pressure on the brain, leading to a range of neurological problems. This medical emergency requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent potential complications.
Causes of Subdural Hematoma:
Subdural hematomas typically result from traumatic head injuries, such as falls, motor vehicle accidents, or assaults, which cause blood vessels to rupture and bleed into the space surrounding the brain. However, in some cases, subdural hematomas can occur spontaneously, particularly in older adults or individuals with a history of alcohol abuse, seizure disorders, or blood clotting disorders.
Symptoms of Subdural Hematoma:
Symptoms of a subdural hematoma can vary depending on the severity of the bleeding and whether it develops quickly (acute) or slowly (chronic). It's essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, especially after a head injury.
Acute Subdural Hematoma:
- Severe headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness
- Confusion or altered mental status
- Slurred speech
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness or coma
Chronic Subdural Hematoma:
- Headache (may worsen over time)
- Gradual decline in mental function
- Personality changes
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty walking or balancing
Diagnosis of Subdural Hematoma:
If you experience any of the above symptoms after a head injury, it's crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing serious complications. Doctors will typically perform a physical examination and ask about your medical history. Imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRI scans, are used to confirm the presence and location of the bleeding.
Treatment of Subdural Hematoma:
The treatment for a subdural hematoma depends on the severity of the bleeding. In some cases, medication may be enough to control swelling and prevent further bleeding. However, for larger hematomas or those causing significant pressure on the brain, surgery may be necessary to remove the clot. Minimally invasive surgical procedures are often preferred.
Observation: Small, asymptomatic subdural hematomas may be monitored closely without intervention, particularly in elderly patients or those with significant medical comorbidities.
Medication:In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to reduce swelling or prevent seizures.
Surgical Intervention: If the hematoma is large or causing significant symptoms, surgical drainage may be necessary to remove the accumulated blood and relieve pressure on the brain. Surgical procedures for subdural hematoma include burr hole drainage, craniotomy, or craniotomy.
Rehabilitation: After treatment, patients may require rehabilitation therapy to regain lost functions and improve their quality of life, particularly if they experience neurological deficits.
Preventing Subdural Hematoma:
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of subdural hematoma, especially those resulting from accidental trauma, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
Wear Protective Gear: When engaging in activities with a risk of head injury, such as sports or recreational activities, wear appropriate protective gear, such as helmets. Use seat belts and child safety seats in vehicles.
Prevent Falls:Take precautions to prevent falls, particularly in older adults, by removing tripping hazards, using handrails on stairs, and installing grab bars in bathrooms.
Manage Medical Conditions: Control underlying medical conditions that increase the risk of bleeding or clotting disorders, such as hypertension or anticoagulant therapy, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Avoid Alcohol Abuse:: Limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of falls and accidents that can lead to head injuries.
Living with Subdural Hematoma:
Recovery from a subdural hematoma depends on the severity of the injury and the individual's overall health. Some people make a full recovery, while others may experience lasting neurological problems. Rehabilitation may be necessary to help regain lost skills and improve function.
Subdural hematoma is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can minimize their risk of developing subdural hematoma and improve their overall brain health and well-being. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms suggestive of subdural hematoma, seek immediate medical evaluation to ensure timely diagnosis and intervention.
For personalized advice and consultation on any brain and spine-related concerns, it is strongly recommended to seek the expertise of a qualified medical professional. We encourage you to consult with Dr. Adarsh Patel, a best neurosurgeon in ahmedabad for their expertise in addressing various neurological and spinal conditions. Dr. Adarsh Patel possesses a wealth of experience and is committed to providing comprehensive and individualized care to patients. To schedule an appointment or seek further guidance, please contact Dr. Adarsh Patel directly Click Here. Your health is of utmost importance, and consulting with a specialist ensures that you receive accurate information tailored to your specific needs.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as, nor should it be considered, a substitute for professional medical advice. Do not use the information on this website for diagnosing or treating any medical or health condition. If you have or suspect you have a medical problem, promptly contact your professional healthcare provider.
